Above polar pattern represents HD800's positioning pattern on my dummy-head, EURI. It is clear that the peak is present at all positions except at the front(90°), where the peak is slighly reduced.
( v / frequency ) = wavelength for fundamental modes
(340,000 mm/s) / 5,000 Hz = 68 mm
(340,000 mm/s) / 6,000 Hz = 57 mm
And considering the role of a quarter-wavelengh resonance, the reflection has to be occuring approximately 14 mm to 17 mm away from the driver in the housing. However, even if the housing is acousically treated with modification, the peak is more or less still present. Then what is the ultimate cause of the peak? Is it possible that the source is from the center hole?
A ring radiator transducer simulated
In order to figure out the effect of a center hole, a Kobitone 25CE500-RO driver has been used for experiment. Its datasheet is here.
Frequency response
A calibrated free-field microphone placed at 10 mm distance
First of all, as a center hole is created in the middle of the diaphragm, the motion break-up of the cone is gone. And the consequential frequency response change is as seen above. The bandwidth remains unaltered, but the high frequency resonances are shifted downwards. And surely enough, a familiar pattern emerges:
Relative difference with the stock as a reference
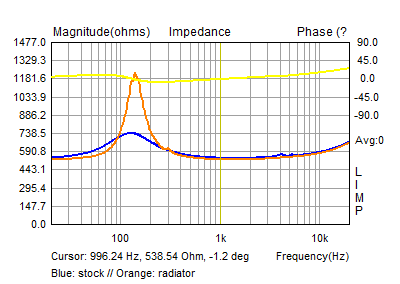
Impedance
The mechanical resonance has been increased by a great degree with an upward shift.
Thiele-Small parameters
| Stock | Radiator | ||
| DC R | Res (Ω) | 550 | 550 |
| Free Air Resonance | Fs (Hz) | 121.01 | 139.4 |
| L of coil | Le (uH) | 2342.59 | 2255.72 |
| L due to ind coupl of eddy current | L2 (uH) | 3427.82 | 1952.33 |
| R due to eddy currents | R2 (Ω) | 44.08 | 52.11 |
| Total Q | Qts | 0.62 | 1.09 |
| Electrical Q | Qes | 2.19 | 1.89 |
| Mechanical Q | Qms | 0.87 | 2.58 |
| Effective mass | Mms (g) | 0.18 | 0.12 |
| Mechanical R of driver loss | Rms (kg/s) | 0.16 | 0.04 |
| Compliance | Cms (m/N) | 0.0096 | 0.011 |
| Air volume equivalent | Vas (liters) | 2.13 | 2.45 |
| Effective area of cone | Sd (cm^2) | 12.57 | 12.57 |
| Force factor | Bl (Tm) | 5.76 | 5.33 |
| Reference efficiency | ETA (%) | 0.17 | 0.34 |
| SPL @ 1 m for 2.83 V | Lp(2.83V/1m) (dB) | 66.1 | 69.27 |
According to Dr.Wolfgang Klippel, mechancal & acoustic losses are dominant source for microspeakers's nonlinear distortion. Thus, the most importance parameters in this analysis are Bl, Cms, and Rms. Compliance of the suspension and mechanical resistance have definitely improved, while the force factor slightly decreased.
Total harmonic distortion
Interestingly, while the overall harmonic distortion figures are pumped up, distortions at 3~4 kHz, at which the human hearing is the most sensitive, have been reduced.
Directivity index
0-degree measurement data as reference
As a ring driver radiates soundwaves more uniformly than a dome, although its perceptual effect is not subjectively evaluated yet, it can be expected that the spatial distribution of a ring driver should be more like that of a electrostatic driver.
The role of a concha
Apart from electroacoustic properties of the driver, it is also vital to look into the physioacoustic properties of our body parts. Naturally, a concha boosts input signal up to 10 dB at 5~6 kHz due to Helmholtz resonance of its own cavity volume.
And of course, if the input signal has a peak at such frequency range, the result can be expected to be even more amplified, just like the case of HD800.
Conclusion
By simulating a ring radiator driver by making a hole in the middle of a Kobitone unit, its electroacoustic effect has been predicted. Thus, it can be assumed that the peak at 5~6 kHz of Sennheiser HD800 is deriving from these causes:
1. Resonant housing
2. Resonance shift due to center hole
3. Concha resonance
While the overall sound signature can be altered with modifications, it is virtually impossible to totally eliminate the peak.
(The deviation between Sennheiser's official frequency response data and conventional HATS measurement data shall be discussed in the next entry, as Gennadiy is expecting to receive the frequency response chart from Sennheiser soon)









The THD seems to be very high, unlike the rest of Sennheiser's headphones you measured, which fitted perfectly the data they posted (0.05%~ for the HD650 and 0.06~ for the IE800). How come there is so much distortion (the data on their site says it should have about 0.02% THD)
ReplyDeleteWhy there is no left and right THD measurements here, unlike the rest of the headphones you measured?
COM International Company
ReplyDeleteSpeakerphone,SP 20 ML,Conferencing,Computer,Smartphone, http://comint.com.hk
http://www.comint.com.hk/en/speakerphone/239-sp-20ml.html
Bluetooth Headset,Headset Smartphones,Headet Mobil Telefon,PRESENCE UC http://comint.com.hk
http://www.comint.com.hk/en/bluetooth/41-presence-uc-ml.html
Bluetooth Business Headset,Bluetooth,MB Pro 2 ML,Noise Cancelling - http://comint.com.hk
http://www.comint.com.hk/....../248-mb-pro-2-uc-ml.html
DW Office,WirelessHeadset,DECT,Personal Audio,sennheiser, http://comint.com.hk
http://www.comint.com.hk/en/wireless-1/34-dw-office-ml.html
Wireless Headset,MB 660 UC MS,Skype for Business,ANC, http://comint.com.hk
http://www.comint.com.hk/en/bluetooth/264-mb-660-uc-ms.html